Solar radiation varies throughout the day. As such it is very important that precise measurement of solar rays is done to design, develop, and analyze the performance of solar power plants. A continuous spatial estimate using a satellite can be done, but the best data collection is done using ground-based measurement instruments. As the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) intends to achieve the target of 20 GW of solar power in India by 2022 under Jawaharlal Nehru National Solar Mission (JNNSM) in 3 phases, solar radiation assessment for India is important for correct assessment and estimation for a solar power project.

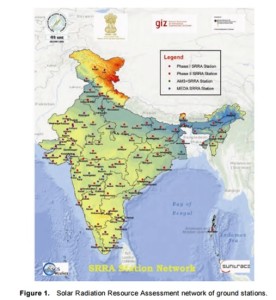
To meet the target MNRE is setting up a network of 115 automatic solar and meteorological measuring stations called Solar Radiation Resource Assessment (SRRA) Stations. The Centre for Wind Energy Technology (C-WET), Chennai, has started a SRRA Unit on mission mode and all 115 SRRA stations were completed in two phases. 4 Advanced Measurement Stations (AMS) with additional sensors are equipped to study effects of suspended particulate matter (turbidity/aerosol concentration) in atmosphere, water vapor, gases, dust particles etc., on scattering or absorption of solar irradiance have been installed at National Institute of Solar Energy (NISE), Gurgaon, Indian Institute of Engineering Science and Technology (IIEST) – Howrah, Pandit Deendayal Petroleum University (PDPU), Gandhi Nagar and Prathyusha Institute of Technology and Management (PITAM), Tiruvallur.
Each of these AMS provide non-stop info on aerosol column, column ozone, atmospheric turbidity, water vapor and NOx in atmosphere. 10 independent narrow wavelength channels between 300 to 1020 nm are constantly monitored for use in UV spectrum analysis. The AMS was set up for quantification of attenuation of solar radiation due to the presence of aerosols in atmosphere and also for measuring the reflectivity of earth (Albedo), atmospheric visibility and incoming long wave radiation for research and development purpose. GIZ, Germany is providing technical assistance to maintain high quality standards on quality measurement, report generation, checks, and Solar Atlas of India.

What is SRRA
SRRA is a large-scale networked project spread across 121 ground stations that involves measurement and collection of data from SRRA stations spread across India under Phase-I & Phase-II program which is archived at the CRS of C-WET. A typical SRRA station consists of two towers of 1.5 m and 6 m height. The 1.5-m tall tower houses a solar tracker equipped with pyranometer, pyranometer with shading disc, and a pyrheliometer to measure global, diffuse, and direct radiation, respectively. The 6-meter tall tower houses equipment to measure temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind speed, direction, rain gauge and data acquisition system. All sensors meet World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and World Radiometric Reference (WRR) standards. The Sun Tracker is configured using GPS system that is always facing the sun.
Each of the SRRA station is equipped with equipment/sensors for measuring Global Horizontal Irradiance (GHI), Direct Normal Irradiance (DNI), Diffuse Horizontal Irradiance (DHI), wind speed & direction, relative humidity, ambient temperature, rainfall and atmospheric pressure. Each SRRA station located mostly at technological universities and engineering colleges across India are powered by a photovoltaic panel with upto 7-day autonomy. The Data Acquisition System records 37 measured and derived parameters each second and transmits data after averaging it to 1 minute directly to the Central Receiving Station (CRS) set up at C-WET. In case of any failure in connectivity, built-in provision has been made to store data for upto 6 months in memory chip, that can be retrieved when needed. A completely automatic quality control procedure is implemented in data processing, analysis and report generation. This includes flagging and gap filling methods using quality check algorithms that directly applies on the raw data.
A dedicated Level 2 server installed at C-WET for applying algorithms specifically developed for data analysis and quality checks based on the raw data collected. For values of Direct Normal Irradiance (DNI), Global Horizontal Irradiance (GHI), and Diffuse Horizontal Irradiance (DHI); applied quality control is based on Baseline Surface Radiation Network (BSRN) rules of World Meteorological Organization (WMO), and elaborated by Management and Exploitation of Solar Resource Knowledge (MESOR).
Data on pyrheliometer error %, azimuth angles, solar elevation, battery voltage and signals on sensor cleaning status are also collected at CRS, C-WET, Chennai. A trigger switch installed track the cleani0ng status of each SRRA stations on daily basis. Reports are generated on daily/monthly/yearly basis once quality assessment has been done. The collection and display of data is done by a specially designed software. Data is monitored in CRS both numerical and graphical format. The collected data is available for use by the solar developers, academics and research and development institutions on payment basis; as per policies of Solar Data Sharing and Policy (SDSAP-2013) of MNRE.
Why Measurement Under SRRA Necessary
- Ground measured data is usually more accurate.
- Quantification of the ground data is possible.
- A combination of measured and satellite data helps better understand the solar potential area.
- Helps in preparation of accurate and reliable SOLMAPS.
- Helps develop & design performance parameters.
- Helps determine the bankability of the solar power proposals.
How SRRA Sites Were Selected
Even though mostly research institutes/academic centers were chosen for installing SRRA stations; but the criteria for selection was as follows:-
- Area
- Free horizon
- Strong network connectivity
- Safety & Security
- Electromagnetic interference
- Easy accessibility to site
How SRRA Works
- The server at CRS went operational on May, 2011.
- The data is transferred from SRRA stations to CRS, Chennai ever since.
- To ensure quality and accuracy of data transmitted to CRS at C-WET, Chennai it is extremely important to maintain the health of each station by properly monitoring them on daily basis.
- As many of SRRA stations are installed in remote areas, the role and commitment of station keepers in upkeep and safety of the instruments and sensors is important.
- The quality of data depends on accuracy and daily maintenance levels of sensors used for measurement. However over time the sensor accuracy levels are bound to change forcing re-calibrations of sensors as per international standard protocol.
- A calibration laboratory at C-WET calibrate field sensors once every two years. The primary standard instruments are to be calibrated against WRR standards at Geneva, Switzerland once in 4 years.
- A specific document has been prepared for calibration as per Indian conditions based on ISO:9847, ISO:9846 and ISO:9059 guidelines.
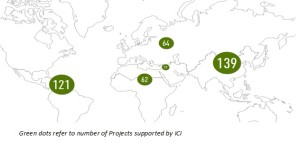
ICI Collaboration for SRRA
The SRRA project works in synergy with SolMap project, funded by International Climate Initiative (ICI) of Federal German Ministry of Environment, Nature Conservation and Nuclear Safety. SolMap is implemented by Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) in co-operation with MNRE. GIZ provides SRRA with technical assistance and capacity building at C-WET that helps the concerned people to maintain desirable standards on quality, checks, report generation. GIZ also supports C-WET in carrying out scientific data analysis as well as generation of value added products. C-WET is also collaborating with other national and international Institutes like Space Application Centre, Ahmadabad; National Renewable Energy Laboratory, USA.
Indian Solar Radiation Atlas

The atlas was launched on 3 June 2015 by National Institute of Wind Energy (NIWE), as an online GIS-based information portal to facilitate expansion of the solar energy sector in India. NIWE is a research institute under MNRE. SolMap Project was the harbinger for setting up Solar Radiation Measuring Network and later morphed into the development of this Atlas. The Atlas presently indicates the annual average values of GHI, DNI, DHI, along with administrative details of ground stations. It also provides details of solar resources at any location with 3 km ´ 3 km spatial resolution. The solar radiation data, collected from the ground stations, are also supported by satellite-derived estimates collected via Meteosat-5 & Meteosat-7 satellites.
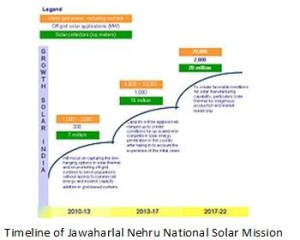
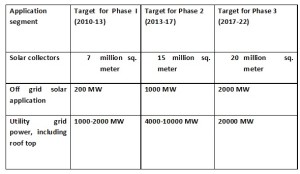
Implementation of National Solar Mission
Government Incentives
As of the end of July 2015, following are the 5 most prominent incentives:-
- Accelerated Depreciation:For profit making enterprises who install rooftop solar systems upto 40% of investment can be claimed as depreciation in the 1st year itself significantly decreasing tax to be paid in Year 1 for profit making companies.
- Capital Subsidies:Capital subsidies are applicable to rooftop solar power plants, up to 500 kW. While the original capital subsidy was 30%, it was recently cut to 15%.
- Renewable Energy Certificates:Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) are tradeable certificates for use as incentive to those who generate green/solar power by providing financial incentives for every unit generated.
- Net Metering Incentives:Net metering incentives depend on
a) whether the net meter is installed
b) the incentive policy of the utility company.
If there is a net metering incentive policy in a state and if there is a net meter on rooftop, then
financial incentives for the power generated is a surity.
- Assured Power Purchase Agreement (PPA):The state and central power distribution and purchase guarantee the purchase of solar power as and when it is produced. The PPAs offer a high price equal to that of the peaking power on demand for solar power which is secondary power or negative load and a intermittent energy source on daily basis.
Solar Data Sharing and Accessibility Policy (SDSAP-2016)
The mechanism for automated data quality control as per international norms is in place for quality control of SRRA data. To provide data to policy makers, solar power developers, R&D institutions; a solar policy was announced by MNRE known as the Solar Data Sharing and Accessibility Policy (SDSAP-2013). The guidelines are given below.
I. General Policy Guidelines
- NIWE operates and maintains SRRA stations as per relevant protocols. The data collected at SRRA field stations are transmitted to CRS at NIWE, Chennai and data is subjected to quality checks and is preserved at multiple locations in raw as well as processed form.
- NIWE will disseminate limited data through its website. The following information is to be made available on the NIWE website:
- Map showing SRRA stations across India with tags, which when clicked by the users will pop out a small window to give stations basic parameters and previous month average values.
- Sample data files for a SRRA station.
- NIWE/NISE is authorized to sell processed data of up to 25 SRRA stations to a single buyer (Indian/ foreign nationals/ R&D institutes/organizations) and receipts are be credited to SRRA account maintained by NIWE. For selling data of more than 25 SRRA stations, specific permission from MNRE is a must.
- Data provided to buyers are for their exclusive use only and the data in full/part or any other form can be disclosed/copied/distributed/transferred/reproduced for use by other agencies either electronically or in a physical form. All parties procuring SRRA data must submit an undertaking as such.
- MNRE is the sole and exclusive owner of the SRRA data, both in raw and processed form received at the CRS at NIWE, Chennai. Access to the data will be guided by the following principles:-
- Access to day-to-day data of each SRRA site for their use is subject to specific signing of Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA).
- Publication of data in any form isn’t allowed, unless otherwise specified with written permission from MNRE through NIWE.
II. Data Policy
- The raw data is available only for collaborative work with national/international Institutions to develop solar maps and other value added products under specific permissions from MNRE. After solar maps are developed these will be examined by a National Solar Radiation Expert Committee (NSREC) which consists of experts from MNRE, ISRO, NIWE, IMD, SEC, SECI, IIT and other well known institutes under Chairmanship of Joint Secretary (NSM),MNRE.
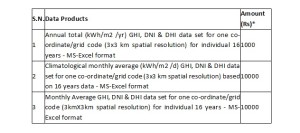
- The cost for various SRRA data products are as follows.

*Above charges would be subject to levy of service tax and any other tax/cess levied by the Government from time to time.
Data from Indian Solar Radiation Atlas
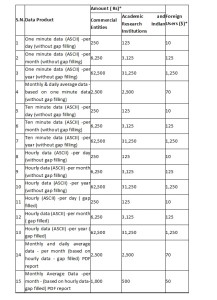
*Above charges would be subject to levy of service tax and any other tax/cess levied by the Government from time to time.
3. The service tax (currently 15%) any other tax /cess as applicable levied by Government from time to time is also to be paid along with the data cost. Data cost including taxes is to be paid in advance.* The revised price for solar data products is w.e.f. 06.05.2016.
4. The cost of data would remain the same even if anyone wants to procure data only for limited number of parameters.
5. Academic/research institutes that procure SRRA data need to send an authorization letter on organizational letter head duly signed by Head of the Institution stating the reason that data is being procured solely for in-house research and will not be shared with any other organization.
6. Buyer should pay the amount only after being satisfying about the quality of the SRRA data.
7. Under no circumstances money once paid for purchase of SRRA data will be returned to the buyer.
8. In case, the buyer remits amount, SRRA can provide data for an equivalent alternate period or alternate stations data.
9. SRRA data would be sold either through CD /e-mail.
About Vivaan Solar
Vivaan Solar as a EPC contractor is a solar PhotoVoltaic system installer & integrator. We have installed 60 MW solar park in Madhya Pradesh, 5 MW in Punjab, 8 MW in Uttarakhand and an upcoming park in Karnataka. We are also MNRE accredited channel partner for Rooftop. We have done turnkey works for multiple companies across the country and has third party agreements with some of the leading industries/commercial institutions across the state. We are an MNRE accredited channel partner. For more info you can visit our website:www.vivaansolar.com or mail info@vivaansolar.com.
Sources
www.solarguidelines.co.in/index.php/srra/
niwe.res.in/department_srra.php
mnre.gov.in/file-manager/akshay-urja/may-june-2014/EN/23-27.pdf
www.eai.in › club
ceew.in/…/Appendix_I-Automatic_Solar_Resource_Monitoring_Stations_in_India.pdf
www.seci.gov.in/upload/…/SolarPACES2013_SolMap_Revision_20130909_1.pdf
www.currentscience.ac.in/Volumes/109/10/1765.pdf


It’s an amazing paragraph designed for all the internet
users; they will get benefit from it I am sure.
dear
sir/madam
Thanks for the appreciation for writing the blog and do spread the word about our blog.
We do like to share useful information on solar power and renewable energy and technology and add our perspective and please share the info with your friends.
Keep watching this space for the latest blog updates and do watch our social media profile.
Hmm is anyone else having problems with the images on this blog loading?
I’m trying to figure out if its a problem on my end or if it’s the blog.
Any feed-back would be greatly appreciated.
dear
sir/madam
Thanks for the appreciation for writing the blog and do spread the word about our blog.
We do like to share useful information on solar power and renewable energy and technology and add our perspective and please share the info with your friends.
Keep watching this space for the latest blog updates and do watch our social media profile.
try to open this blog in a different browser after deleting the cache